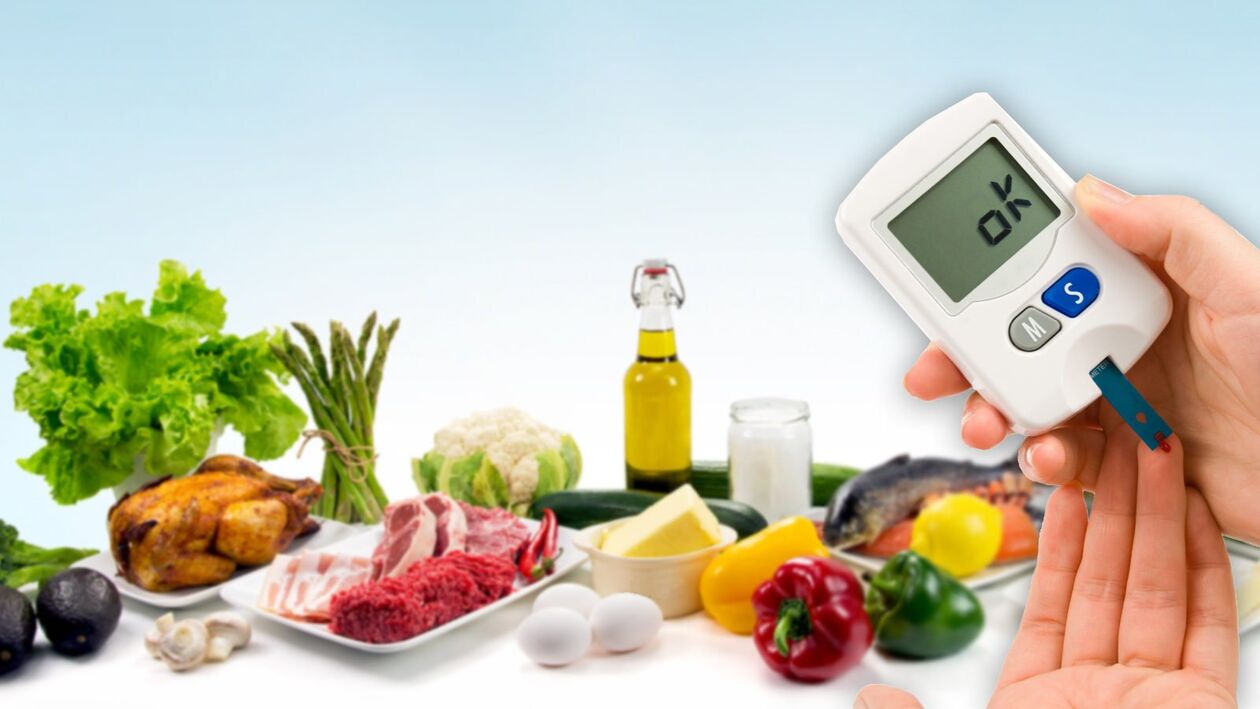
A diet for diabetes is not just a recommendation to improve the quality of life, but a necessity. Every patient should follow the nutritional advice. This is necessary to minimize the risks of acute complications, as well as worsening the general condition.
A balanced diet allows you to establish metabolic processes in the body, which is extremely important when diagnosed with diabetes. The disease poses a potential threat to life, since it can be accompanied by critical conditions: ketoacidosis, failure of internal organs, hypoglycemia and others. For the sake of their own health, the patient must understand not only the essence of the disease itself, but also its effect on the body. This will help you organize a rational menu, develop healthy habits and learn to take your doctor’s prescriptions seriously.
Etiology and pathogenesis
The first information about diabetes known to science dates back to the Hellenic period. Of course, the ancient Greeks did not have diagnostic capabilities and did not know the nature of the disease. But already in those days (IV-I centuries BC) doctors tried to systematize information about symptoms and therapy.
According to WHO, today the disease affects about 4% of people, and it claims 3 million lives a year, which exceeds the figures for AIDS.
The disease has multiple etiologies and is accompanied by a wide range of symptoms. It is based on insulin deficiency, which can be absolute or relative.
Etiology of diabetes:
- overweight;
- injuries – physical and mental;
- viral diseases that caused complications;
- aggravated heredity;
- autoimmune diseases.
Provoking factors include prolonged frequent stress and poor eating habits. People who often overeat are at risk by including excessive amounts of carbohydrates and sugar in their menu.
In the pathogenesis, the main role is played by disruption of the islet apparatus of the pancreas, as a result of which insulin is produced in abnormally small quantities or not produced at all.
Symptoms of diabetes:
- general weakness;
- weight loss;
- increased urine production, frequent urination;
- slow wound healing;
- decreased libido;
- itching of mucous membranes;
- deterioration of hair and nails;
- increased appetite, constant thirst.
The disease is one of those that requires mandatory therapy. It is impossible to fight the symptoms of diabetes with folk remedies. Seeing a doctor is necessary, and the earlier the diagnosis is made, the more favorable the prognosis. In addition to the medication course, a rational nutrition system is required.
Classification of the disease and the role of nutrition
The diet is determined by the degree of inhibition of the pancreas itself.
The disease is classified as follows:
- Type I diabetes is an autoimmune disease and a relatively rare form. It is characterized by an extremely low level of insulin production; in some cases, the patient’s body does not produce this hormone at all. Patients are forced to take injections on a regular basis, which is why the term "insulin dependence" is also used. A diet aimed at lowering glucose levels helps improve well-being and avoid the risk of hypoglycemia.
- Diabetes II occurs in 90% of cases. It often develops in people who are overweight and have a sedentary lifestyle, who do not watch their diet and consume plenty of foods that increase glucose levels (flour, potatoes, sweets). The diet should be structured so that the weight gradually returns to normal. Moderate physical activity is recommended for such patients.
- Gestational diabetes is a disease that can develop in pregnant women, especially with severe toxicosis in the second trimester. The diet for gestational diabetes should contain a sufficient amount of dietary supplements and careful control of body weight. In most cases, after pregnancy ends, health returns to normal, but there is a risk of developing type II diabetes. To avoid this, you should follow the recommended diet after childbirth.
In 1% of cases, other types of the disease develop: latent, steroid, neurogenic, renal, MODY, bronze and prediabetes. The diet for a type of diabetes included in one of these categories is determined by the attending physician, taking into account many factors.
Types of diets for diabetes
The basis of therapy in the treatment of diabetes mellitus is a course of medication aimed at reducing glucose levels and restoring normal insulin levels. At the same time, doctors insist on the importance of moderate physical activity and proper nutrition.
About 80% of patients are overweight. Often, excess body weight exceeds normal levels by 15 percent or more. When weight is normalized, patients' general condition noticeably improves: blood pressure stabilizes, the functioning of the nervous system improves, the level of chronic fatigue decreases, and well-being improves. But with such a diagnosis, extreme methods of quickly getting rid of extra pounds are strictly contraindicated, and many, even the most popular, diets are not suitable for patients with diabetes. You cannot choose a power system based on reviews from friends or even recommendations from experts on the Internet. Experimenting with "proven" diets, such as, for example, the Kremlin or Dukan, can lead to the fact that the metabolism goes wrong even more. Namely, efforts should be directed towards restoring the normalization of metabolic processes.
Types of nutrition programs
- A protein diet is aimed at suppressing appetite by providing the body with a large amount of protein, which stimulates the production of biologically active substances. Proteins of plant and animal origin are introduced into the diet in equal proportions. Red meat is prohibited; it is replaced by fish, lean poultry, dairy products and protein-rich beans and grains.
- A low-carbohydrate diet for diabetes, based on vegetables and fruits containing complex carbohydrates. Simple carbohydrates are prohibited, and proteins are introduced in limited quantities. This nutrition system is considered strict, and it is used when the blood sugar level increases significantly - 3 times or more.
- A low-carbohydrate diet is more gentle and is suitable for those who suffer from type I and type II diabetes.
- The buckwheat diet is indicated for normalizing metabolic processes and saturating the body with vitamins, macro- and microelements.
- A preventative diet is based on replacing red meat with lean, protein-rich foods, using proper cooking methods and consuming fiber.
- The Bernstein diet is indicated for type 2 diabetes mellitus, as well as for prevention. This is not just a menu, but an integrated approach to organizing a balanced diet, which can be taught to even small children.
Carbohydrate counting
Bread unit is a concept familiar to every diabetic patient. This is a conventional unit of measurement (XU), which corresponds to 10-13 g of carbohydrates and is used when calculating the calorie content of foods. The patient can take 4-6 XE per meal.
1 XE corresponds to:
- 1 tbsp. l. sugar or honey;
- 150 ml juice;
- 130 g orange;
- 60 g banana;
- 100 g melon;
- porridge – 2. 5 tbsp. l. raw cereals;
- milk and fermented milk drinks – 250 ml;
- 20 g dried fruits.
It is also important to consider the type of food and how it is prepared. For example, low-fat fish fillets are allowed in limited quantities in some diets, but fatty canned fish are prohibited for all patients.
Diet for type 1 diabetes
Type 1 diabetes requires a diet that will maintain blood glucose levels at 3. 5-5. 5 mmol/liter.
Diet principles:
- Fractional nutrition of the patient: 5-6 meals per day.
- The maximum daily calorie content is 2000 kcal.
- Carbohydrates for breakfast, lunch and dinner.
- Minimum snack at night.
- Fast carbohydrates are prohibited.
- Refusal of sugar, replacement with safe analogues (stevia, synthetic sweetener).
- Long-acting insulin preparations are administered before meals, short-acting insulin preparations are administered after meals.
- The maximum amount of XE per meal is 8.
- Natural products are a priority.
Allowed are yeast-free baked goods, soy cheese and milk, unsweetened green tea, dried fruit compote, fresh fruits and vegetables, nuts, and cereals. Many vegetarian dishes are suitable for the diet.
Rich first courses and roasts, fatty meats and fish, smoked meats, pasta, and fast food are prohibited. Alcohol, especially red wine, is strictly prohibited.
Diet for a week for insulin-dependent people with excess weight
Day No. 1
- A slice of bread, porridge, soft cheese, tea.
- Orange, pistachio.
- Borscht, salad, stewed cabbage, cutlet, lavash.
- Rosehip, cottage cheese, fruit jelly.
- Steamed cauliflower, salad.
- A glass of milk.
Day No. 2
- Steamed veal, tomato, grain bread, tea.
- Cheese, half a ripe pear.
- Chicken breast, pumpkin puree, salad.
- Grapefruit, kefir.
- Boiled fish, stewed cabbage.
- Cracker.
Day No. 3
- Lavash, coffee, cabbage rolls.
- Strawberries, yogurt.
- Solid pasta, salad, steamed fish.
- Orange, compote.
- Cottage cheese casserole.
- Kefir.
Day No. 4
- Porridge, cheese, boiled egg, tea.
- Toast with soft cheese, boiled turkey.
- Vegetable puree soup, stewed meat with vegetables, bread.
- Tea with cookies.
- Green beans with chicken breast, rose hips.
- Bread.
Day No. 5
- Cottage cheese with kefir.
- Pumpkin seeds, raisins.
- Potatoes, salad, compote.
- Baked pumpkin, rosehip.
- Salad, pancakes on rye flour.
- Kefir.
Day No. 6
- Egg, lightly salted salmon, tea.
- Cottage cheese, carrots.
- Borscht with sorrel, vegetarian cabbage rolls, lavash.
- Kefir, bread.
- Stewed eggplants with chicken fillet, fresh green peas.
- Crackers.
Day No. 7
- Porridge with ham, tea.
- Salad with tuna and vegetables, whole grain bread.
- Cabbage soup, stewed vegetables with meat, bread.
- Cottage cheese, plums.
- Squid schnitzel, compote.
- Milk.
Diet for type 2 diabetes mellitus
The point is to reduce animal fats and simple carbohydrates. It is recommended to take a break of no more than 4 hours between meals. This nutrition program is called "Diet No. 9" or "Table No. 9" and is suitable not only for patients, but also for all those who seek to normalize their diet.
Diet for every day for type 2 diabetes
Day No. 1
- Asparagus, quail egg omelette.
- Salad of nuts, apples and boiled squid.
- Beetroot soup, baked eggplants.
- Avocado, cocoa.
- Salmon steak with sauce.
Day No. 2
- Oatmeal, yogurt, apple.
- Smoothie.
- Baked meat (veal) with vegetables.
- Cottage cheese casserole.
- Vegetable salad with avocado.
Day No. 3
- Fried egg with cheese, tomatoes and herbs.
- Steamed vegetables with hummus.
- Puree vegetable soup, chicken cutlets, fresh peas.
- Pear and almond.
- Salmon with spinach, yogurt.
Day No. 4
- Baked apples.
- Toast with leafy greens and tuna.
- Beef steak, vegetable salad, parmesan.
- Fruit sorbet.
- Broccoli casserole.
Day No. 5
- Orange, soft cheese, grain bread, fruit tea.
- Beet salad with nuts and butter.
- Steamed fish, rice, grapefruit.
- Berries with cream.
- Squid schnitzel, rosehip.
Day No. 6
- Carrot-curd soufflé.
- Baked broccoli.
- Lenten borscht, baked chicken fillet, leafy greens, tangerine.
- Berry mousse.
- Fish with a side dish of steamed vegetables.
Day No. 7
- Baked apple with raisins, oatmeal and nuts.
- Salad with vegetables and shrimp.
- Polenta, boiled fish, greens, kiwi.
- Strawberries with cream cheese.
- Cucumber and herb salad, tea.
Diet for gestational diabetes
Gestational diabetes occurs due to disruption of the pancreas during pregnancy. The expectant mother should adhere to the following nutritional principles:
- Exclude flour, baked goods, any store-bought sweets, semolina porridge and any products with sugar.
- BJU norm: 20 |30 |50 %. You need to balance your diet based on these indicators.
- Include fruits, dairy and starchy foods in your diet.
- Strictly observe the drinking regime. It is necessary to consume 1. 8-2 liters of drinking water per day.
- Organize 3 main meals and 2 snacks per day.
- Minimize the consumption of coffee and tea (no more than 2 cups per day).
- Take special vitamin complexes as recommended by your doctor.
- Introduce herbal remedies into your diet to reduce sugar: decoctions of linden flowers, blueberry leaves, lilac buds, celery root.
Low-carbohydrate diets are not suitable for pregnant women. The norm of calorie consumption per day is 2000-2500 kcal.
Recommended menu for expectant mothers with high blood glucose
To control glucose levels, it is recommended to build a menu based on the following scheme.
- Breakfast: porridge (oatmeal, millet, buckwheat), grain bread, tea or dried fruit compote.
- Second breakfast: toast with unsalted cheese, apple.
- Lunch: porridge, vegetable salad, stew (beef or chicken).
- Afternoon snack: cottage cheese, cracker, orange.
- Dinner: vegetable side dish, boiled meat, juice, cracker or pita bread.
3 hours before bedtime, you can drink a glass of yogurt or kefir. In addition to diet, it is important to take walks, warm up if possible, and do simple exercises at home or with a trainer.
Diet for insulin-dependent diabetes in children
Children suffer more severely from the disease than adults, and the incidence of type 1 diabetes in this age group is higher - up to 80%. Children at risk (whose family members have diabetes) require careful monitoring of their health status from birth.
Diet for diabetes in children
The rules for organizing nutrition for insulin-dependent children are even more strict than for adults. Approximate diet for a child:
- Confectionery, sweets, baked goods, sweet soda are prohibited. Sugar should be completely eliminated from the diet.
- Fresh vegetables and fruits are allowed, but you need to be aware of the exceptions. A child with diabetes should not be given bananas, dates, persimmons, raisins, grapes, or figs.
- You should organize 6 meals and feed the child strictly according to the hour. The deviation should not exceed 20 minutes. If it is impossible to eat a full meal, you should give your baby a snack of fruit, bread or toast. Insulin-dependent children should absolutely not starve.
- Monitor your fructose consumption and use this indicator as a basis when calculating the permissible amount of sweetener.
- An attack of hypoglycemia can be stopped with a piece of dark chocolate. An accompanying adult is advised to carry this product with them at all times.
- Diet is important. The daily norm is calculated depending on the age and body size of the child by the treating endocrinologist.
It is necessary to organize a correct lifestyle in general. The child must be able to move and be physically active. Constant monitoring of glucose levels and regular consultation with a doctor are also necessary.
Healthy recipes for diabetes
Dietary recipes are suitable not only for the diet of a patient with diabetes, but also for anyone who wants to balance the menu, including healthy foods. Recommended dishes are prepared from simple ingredients, but look presentable and have a rich taste.
Vegetarian cream soup
Prepare and chop one onion, 100 g spinach, 300 g broccoli and 200 g each of celery and zucchini. Blanch for 15 minutes in 500 ml water, puree using a blender. Add 200 ml of milk and 100 ml of cream to the vegetable mass, bring to a boil, adjust the salt.
Vegetable salad
Chop 200 g cabbage. Cut 2 cucumbers into half rings, 2 tomatoes into slices. Mix vegetables, add salt, season with olive oil.
Squid schnitzel with onions
Pass the squid fillet (400 g) through a meat grinder, add 25 g of breadcrumbs to the minced meat. Chop leeks (50 g) and one onion, fry in a frying pan until half cooked. Finely chop the greens - spinach, dill, parsley. Mix the ingredients, knead the minced meat, form schnitzels. Brush each with egg, roll in breadcrumbs and fry for 2 minutes on each side.
Pancakes with blueberries on rye flour
Pour 2 g of stevia into a glass of boiling water and let it brew. Mix 200 g of cottage cheese, stevia tincture, 1 egg, 150 g of blueberries. Carefully add 200 g of rye flour, 0. 5 tsp. soda and 2 tbsp. l. sesame oil. Fry the pancakes in a non-stick frying pan on both sides.
Cauliflower zrazy
Boil 500 g of cauliflower inflorescences for 10 minutes, cool and chop with a blender. Add 4 tbsp. l. rice flour, salt, let it brew for 30 minutes so that the fiber dissolves. Boil and finely chop 2 eggs, add chopped green onions. Form flat cakes from the vegetable mass, place the egg and onion filling inside, and decorate with zrazy. Roll in rice flour and fry in a frying pan.
Cottage cheese and pear casserole
Mix 600 g of low-fat cottage cheese, 2 eggs and 2 tbsp. l. rice flour, knead thoroughly. Peel and chop 600 g of pears: finely chop half of them into cubes, grate the other half. Mix the pears with the curd mass, let it brew for 30 minutes. Place in a silicone mold, grease with sour cream, bake for 45 minutes at 180 degrees.
Cottage cheese and carrot soufflé
Grind 200 g of cottage cheese, add 300 g of grated carrots. Grind 50 g of walnut kernels, 3-4 sprigs of parsley, add to the mixture. Add 2 yolks, then 2 beaten whites. Pour the batter into silicone muffin molds, filling 2/3 full. Bake for 20 minutes.
The preparation of a patient’s menu should be taken responsibly. It should not only be balanced, but also varied in order to prevent breakdowns in unhealthy foods or refusal to eat. A systematic approach will help maintain health, prevent deterioration and significantly improve the quality of life.